 Quantum computing isn’t a buzzword anymore. It’s a real shift in how humans solve problems that classical computers simply cannot touch. For decades, we made computers faster by shrinking transistors. That trick is running out of road. At the same time, our problems have exploded in complexity. Climate modeling. Drug discovery. Cybersecurity. Artificial intelligence. These aren’t just bigger spreadsheets. They’re fundamentally hard problems.
Quantum computing isn’t a buzzword anymore. It’s a real shift in how humans solve problems that classical computers simply cannot touch. For decades, we made computers faster by shrinking transistors. That trick is running out of road. At the same time, our problems have exploded in complexity. Climate modeling. Drug discovery. Cybersecurity. Artificial intelligence. These aren’t just bigger spreadsheets. They’re fundamentally hard problems.
Here’s what matters. Quantum computing doesn’t try to beat classical computers at everyday tasks. Your phone, laptop, and cloud servers will still do what they do best. Quantum machines step in when the math becomes overwhelming, when trillions of possibilities must be explored at once. That’s where everything changes.
This article explains quantum computing without the physics headache. You’ll see what it is, how it works, real examples, why 2026 keeps coming up, and what it actually means for the world you live in.
Why Quantum Computing Matters Right Now
The timing is not accidental. Global data creation is growing faster than our ability to analyze it. According to multiple industry reports, more than 90 percent of the world’s data was created in the last few years alone. Classical computers process data step by step. That approach breaks down when problems scale exponentially.
Quantum computing attacks the problem differently. Instead of checking one solution after another, it explores many possibilities at the same time. That single shift rewrites what is computationally possible.
Governments are investing billions. Tech giants are racing to stabilize hardware. Universities are producing a new generation of quantum engineers. This isn’t theoretical curiosity anymore. It’s strategic infrastructure, like electricity or the internet once was.
Bottom line: quantum computing matters now because the limits of classical computing are becoming visible everywhere.
What Is Quantum Computing? A Simple Explanation
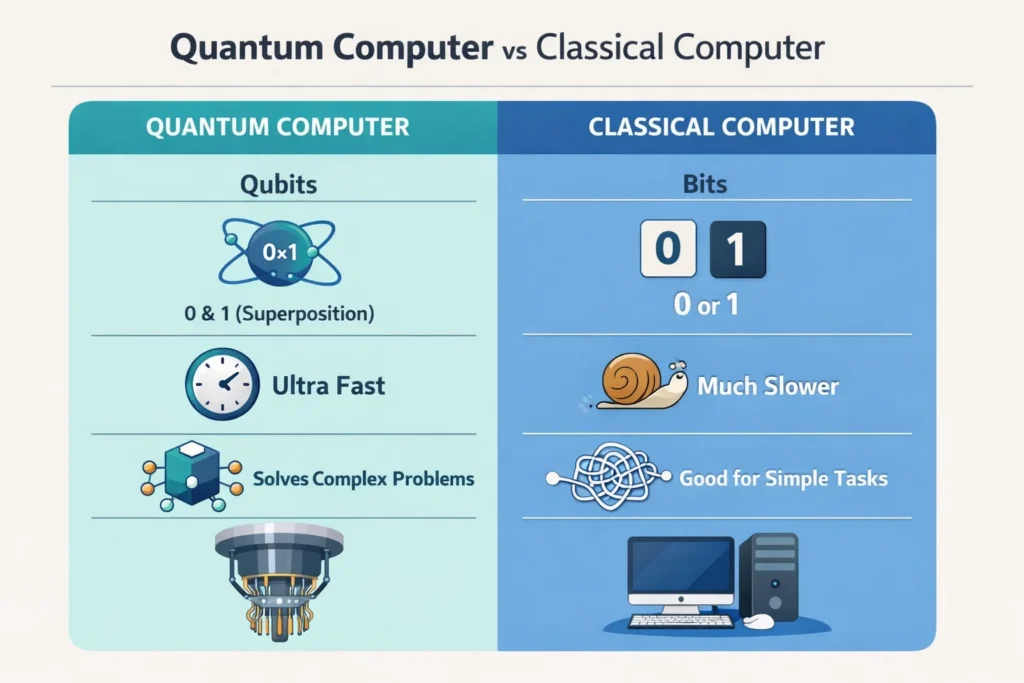
Quantum computing is a new way of processing information using the rules of quantum physics instead of classical physics.
A normal computer uses bits. Each bit is either a 0 or a 1. Everything you see on a screen, from videos to bank transfers, boils down to long strings of these binary choices.
A quantum computer uses qubits. A qubit can be 0, 1, or both at the same time. This property is called superposition. It sounds abstract, but the effect is practical. One qubit can represent multiple possibilities at once.
Now multiply that across dozens or hundreds of qubits. The number of states a quantum system can explore grows astronomically. This is why quantum computers don’t just run faster. They solve a different class of problems entirely.
A good analogy is a maze. A classical computer tries one path at a time. A quantum computer explores many paths simultaneously and interferes with itself to amplify the best answer.
How Quantum Computing Works Behind the Scenes
Three ideas power quantum computing: superposition, entanglement, and interference.
Superposition allows a qubit to exist in multipe states at once. Until it’s measured, it’s not locked into a single value. This creates parallelism at the hardware level, not through software tricks.
Entanglement links qubits together. Change the state of one, and the others respond instantly, even if separated. This creates correlations that classical systems can’t replicate.
Interference is how quantum computers get useful answers. Wrong paths cancel out. Right paths reinforce each other. The system is engineered so the correct solution becomes the most likely outcome when measured.
Here’s the catch. Quantum systems are fragile. Heat, vibration, or electromagnetic noise can destroy qubit states. That’s why quantum computers operate near absolute zero and require heavy error correction.
Quantum computing isn’t magic. It’s precision engineering at the edge of physics.
Quantum Computing With Example
Imagine designing a new drug.
Classical computers simulate molecules by approximating interactions. That works for small systems, but real biological molecules are chaotic at scale. The math explodes.
Quantum computers model molecular behavior naturally because molecules themselves follow quantum rules. Instead of approximating chemistry, quantum systems simulate it directly.
In practice, this means faster identification of promising compounds, fewer failed lab experiments, and shorter development cycles. What takes years could take months.
Another example is traffic optimization in large cities. Millions of variables change in real time. Quantum algorithms can evaluate vast combinations simultaneously, identifying traffic patterns that classical systems struggle to see.
These aren’t science fiction demos. They’re early applications already being tested by organizations like IBM and Google.
Advantages of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing’s advantages are not about replacing existing systems. They’re about unlocking new capabilities.
First, speed for specific problems. Optimization, simulation, and cryptography tasks see exponential gains under the right conditions.
Second, accuracy. Quantum simulations reduce approximation errors in chemistry, physics, and materials science.
Third, efficiency. Solving complex problems in fewer steps can reduce energy and time costs across industries.
Fourth, innovation leverage. Entire fields, from battery design to AI training, gain new tools that were previously impossible.
Quantum advantage doesn’t mean universal superiority. It means targeted breakthroughs where classical methods stall.
Uses of Quantum Computing Across Industries
Healthcare uses quantum computing to model proteins, accelerate drug discovery, and personalize treatments.
Finance applies it to portfolio optimization, fraud detection, and market simulation under extreme conditions.
Energy and climate science rely on quantum models to simulate chemical reactions, carbon capture materials, and weather systems with higher fidelity.
Artificial intelligence benefits from faster optimization and improved training of complex models.
Cybersecurity both fears and uses quantum computing. It threatens current encryption but also enables quantum-safe cryptography.
Each industry uses quantum tools differently, but the pattern is the same. When complexity overwhelms classical computing, quantum methods step in.

How Does Quantum Computing Change the World?
Quantum computing changes the world quietly at first. It reshapes research pipelines, national security strategies, and industrial design processes long before consumers notice.
Medical breakthroughs arrive faster. Supply chains become more resilient. Energy systems grow more efficient. AI systems become smarter with less data.
There’s also a geopolitical dimension. Countries that lead in quantum technology gain strategic advantages in defense, intelligence, and economic competitiveness.
This isn’t about faster apps. It’s about changing what humanity can model, predict, and design.
What Does Elon Musk Say About Quantum Computing?
Elon Musk has taken a cautious stance. He acknowledges quantum computing’s potential but warns against hype. His position is grounded in engineering reality. Scaling quantum systems is brutally hard.
That skepticism is healthy. It keeps expectations aligned with physics rather than marketing. At the same time, Musk has supported quantum research through broader investments in advanced computing and AI infrastructure.
The takeaway is balance. Quantum computing is transformative, but it’s not instant or universal.
Why Is 2026 a Quantum Year?
2026 appears repeatedly in industry roadmaps for a reason.
Hardware milestones are converging. Error rates are dropping. Qubit counts are crossing thresholds where useful applications become practical.
Governments are aligning funding cycles with deployment goals. Enterprises are preparing hybrid systems that combine classical and quantum workflows.
Most importantly, software ecosystems are maturing. Developers can now experiment without being physicists.
2026 isn’t a finish line. It’s a tipping point where quantum computing shifts from experimental to operational in targeted domains.
Challenges Holding Quantum Computing Back
Quantum computing faces real obstacles.
Stability remains the biggest challenge. Qubits are fragile, and error correction is resource intensive.
Cost is another barrier. These machines are expensive to build, operate, and maintain.
Talent shortages slow progress. Quantum engineers need expertise across physics, computer science, and mathematics.
Finally, integration matters. Quantum systems must work alongside classical infrastructure, not replace it.
Progress is steady, but patience is required.
What the Future Looks Like After Quantum Breakthroughs
The future isn’t purely quantum. It’s hybrid.
Classical computers handle everyday workloads. Quantum processors accelerate specific tasks in the background. Cloud access makes quantum power available without owning hardware.
Businesses that prepare early gain advantages in optimization, research, and strategy. Those that ignore it risk falling behind when competitors solve problems faster and cheaper.
Quantum computing won’t touch your daily routine tomorrow. But it will reshape the systems you rely on, from medicine to energy to security.
Final Thoughts Before You Try to Understand Quantum Computing Yourself
Quantum computing is not hype. It’s not magic either. It’s a tool that expands the boundaries of what humans can compute.
You don’t need to master quantum physics to understand its impact. You just need to know this. When problems become too complex for classical machines, quantum computing opens doors that were previously locked.
That’s why it changes everything.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is quantum computing in simple words?
Quantum computing is a new type of computing that uses quantum physics instead of normal binary logic. Unlike regular computers that process one possibility at a time, quantum computers can explore many possibilities at once, which helps them solve very complex problems faster.
What is a quantum computer?
A quantum computer is a machine that uses qubits instead of bits to process information. These qubits can exist in multiple states at the same time, allowing the computer to perform calculations that would take classical computers thousands or even millions of years.
How does quantum computing change the world?
Quantum computing changes the world by solving problems that were previously unsolvable. It helps researchers design new medicines, improve climate predictions, optimize global supply chains, strengthen cybersecurity, and push artificial intelligence to new levels.
Can quantum computers replace normal computers?
No. Quantum computers are not meant to replace normal computers. Classical computers will still handle everyday tasks like browsing, gaming, and office work. Quantum computers are used only for specific problems where classical systems struggle.
What are real examples of quantum computing?
Real examples include simulating molecules for drug discovery, optimizing financial portfolios, improving traffic flow in large cities, and modeling climate systems. Companies and research labs already use early quantum systems for testing and experimentation.
What are the advantages of quantum computing?
The main advantages include faster problem solving for complex calculations, more accurate simulations, better optimization results, and the ability to analyze massive datasets that overwhelm traditional computers.
What are the uses of quantum computing today?
Today, quantum computing is used in research labs, universities, and pilot projects across industries such as healthcare, finance, energy, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. Most uses are still experimental, but progress is accelerating.
Why is 2026 considered a quantum year?
2026 is considered a quantum year because many experts expect major breakthroughs in hardware stability, lower error rates, better software tools, and wider business adoption. It’s seen as the point where quantum computing becomes practically useful, not just experimental.
What does Elon Musk say about quantum computing?
Elon Musk has expressed cautious optimism about quantum computing. He acknowledges its potential but warns against exaggeration, pointing out that building stable, scalable quantum systems is extremely difficult and will take time.
Is quantum computing dangerous for security?
Quantum computing could break some current encryption methods in the future. However, it also helps develop quantum-safe encryption, which is designed to protect data even against quantum attacks. Security experts are already preparing for this transition.
Will quantum computing affect everyday people?
Not directly at first. Most people won’t use a quantum computer themselves. However, they will benefit from faster medical breakthroughs, smarter AI systems, better energy solutions, and more efficient technologies powered by quantum computing behind the scenes.
Do I need physics knowledge to understand quantum computing?
No. You don’t need to understand quantum physics deeply to grasp what quantum computing does. Understanding the basic ideas and real-world impact is enough to follow how it’s changing technology and society.
