 Here’s what matters. Blockchain is no longer a buzzword chasing relevance. By 2026, it becomes infrastructure. Quiet, embedded, and hard to oll back. The loud speculation phase fades. What replaces it is adoption where it makes economic sense.
Here’s what matters. Blockchain is no longer a buzzword chasing relevance. By 2026, it becomes infrastructure. Quiet, embedded, and hard to oll back. The loud speculation phase fades. What replaces it is adoption where it makes economic sense.
Governments test it for records. Banks use it for settlement. Supply chains rely on it for trust. Healthcare experiments with it for data ownership. None of this looks dramatic on the surface. But underneath, it rewires how value and information move.
This article breaks that down. No hype. No token price obsession. Just where blockchain actually disrupts traditional industries, why 2026 matters, and where real opportunities sit.
Why Blockchain Still Matters Going Into 2026
Global enterprise spending on blockchain keeps rising even as headlines cool. According to forecasts frequently cited by Gartner, blockchain-enabled business value crosses hundreds of billions of dollars before the decade ends. That growth doesn’t come from retail traders. It comes from logistics firms, banks, insurers, and governments modernizing systems built decades ago.
Traditional databases assume trust. Blockchain assumes none. That single design choice changes everything.
In a global economy where transactions cross borders instantly, trust becomes the bottleneck. Paper trails move slowly. Central authorities fail. Data silos don’t talk. Blockchain removes intermediaries not to be rebellious, but to be efficient.
By 2026, most users won’t even know they’re using it. That’s the point.
Is Blockchain Really a New Technology?
Short answer: no. Practical answer: it’s finally mature.
The foundations go back over a decade, popularized by Bitcoin in 2009. Early systems proved decentralization worked, but they were slow, expensive, and hard to scale.
What changes by 2026 is tooling. Better consensus models. Layer-2 networks. Privacy-preserving cryptography. Cleaner integration with existing software stacks.
Think of blockchain less like a new app and more like the internet in the late 1990s. The protocol exists. The use cases are catching up.
How Blockchain Is Revolutionizing Traditional Business Networks
Traditional business networks rely on reconciliation. Every party keeps its own records, then spends time proving they match. Blockchain flips that model.
One shared ledger. One version of truth. Everyone sees the same state.
Smart contracts replace manual enforcement. Settlement happens in minutes, not days. Audits become continuous instead of annual.
This matters most in environments where multiple parties don’t fully trust each other but still need to cooperate. That’s most of the global economy.
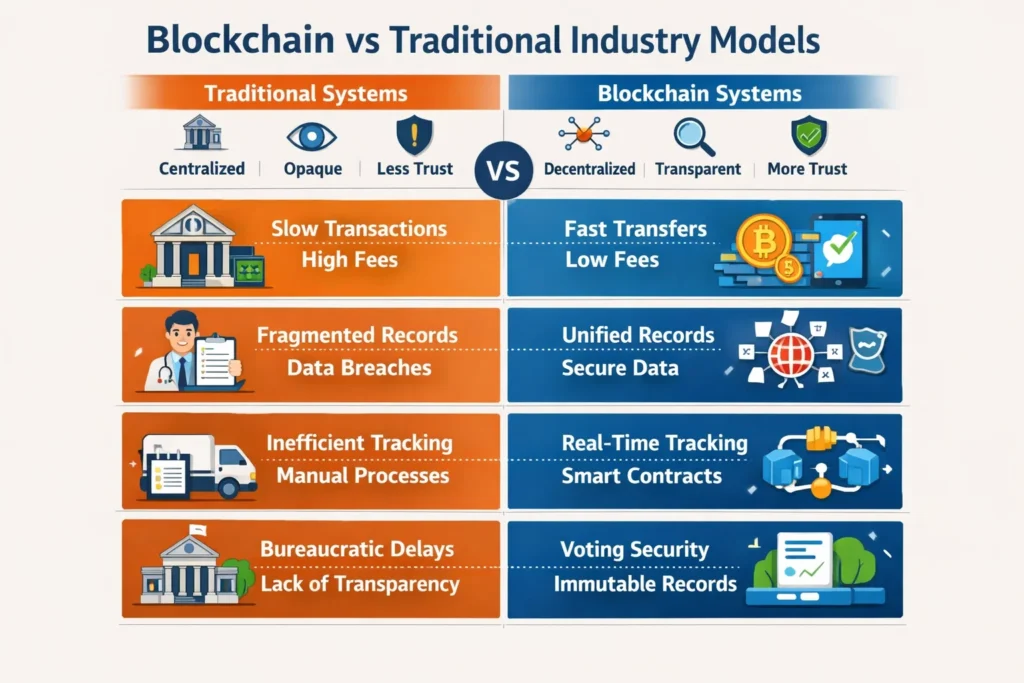
Industries Most Likely to Be Disrupted by Blockchain by 2026
Financial Services and Banking
Banks don’t disappear. Their plumbing changes.
Blockchain reduces settlement risk, cuts cross-border payment costs, and speeds clearing. Central Bank Digital Currencies expand quietly, not to replace cash overnight, but to modernize settlement rails.
Public chains like Ethereum coexist with permissioned networks built for compliance. Decentralized finance influences architecture even when institutions avoid the label.
The disruption isn’t ideological. It’s operational.
Healthcare and Medical Records
Healthcare runs on fragmented data. Blockchain doesn’t store medical files directly. It coordinates access.
Patients gain control over permissions. Providers verify data integrity instantly. Researchers access anonymized datasets without compromising privacy.
The result is fewer errors, better continuity of care, and less administrative drag.
Supply Chain and Logistics
Supply chains break when trust breaks.
Blockchain tracks goods from origin to shelf. Every scan updates a shared ledger. Fraud drops. Recalls become precise. Disputes resolve faster.
Food safety, pharmaceuticals, and high-value manufacturing lead adoption because the cost of failure is high.
Real Estate and Property Ownership
Property records are messy in many parts of the world. Blockchain creates tamper-resistant land registries.
Tokenization allows fractional ownership. Transactions close faster. Paperwork shrinks.
This doesn’t eliminate lawyers. It eliminates redundant verification.
Government and Public Services
Governments adopt blockchain quietly. Identity systems. Licensing. Procurement tracking.
The benefit isn’t decentralization for its own sake. It’s auditability. When records are immutable, corruption becomes harder to hide.

Traditional Systems vs Blockchain Impact
| Problem | Traditional System | Blockchain Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data duplication | Multiple private databases | Single shared ledger |
| Slow settlement | Days or weeks | Minutes |
| Trust disputes | Manual reconciliation | Cryptographic proof |
| Fraud detection | Reactive audits | Real-time verification |
Will Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Disrupt Traditional Financial Systems?
Yes, but not by replacing banks with memes.
Cryptocurrency introduces programmable money. Blockchain introduces programmable trust. Together, they force financial systems to modernize.
Banks adopt the tech without adopting the ideology. That’s fine. Disruption doesn’t require destruction.
By 2026, the biggest impact sits behind the scenes: faster settlement, lower costs, fewer intermediaries.
Blockchain Future Trends to Watch in 2026
Interoperability becomes mandatory. Isolated chains fade.
Layer-2 solutions handle volume. Privacy tech like zero-knowledge proofs enables compliance without exposure.
Enterprises stop asking “should we use blockchain?” and start asking “where does it outperform databases?”
Upcoming Blockchain and Emerging Crypto Technologies
Smart contracts evolve into modular systems. Tokenized real-world assets move beyond pilots. AI integrates with blockchain for automated compliance and monitoring.
Crypto becomes less about coins and more about infrastructure.
Top Blockchains Shaping the Future
This isn’t about rankings by market cap. It’s about relevance.
Networks focused on security, scalability, and developer ecosystems dominate. Ethereum remains influential. Others specialize in payments, data, or enterprise use cases.
The winners solve real problems, quietly.
Blockchain Opportunities for Businesses and Professionals
Opportunities shift from speculation to execution.
Businesses streamline operations. Developers build middleware. Governments modernize records. Professionals who understand both systems and incentives stay in demand.
Blockchain rewards those who think in workflows, not tokens.
Challenges That Could Slow Adoption
Scalability improves but isn’t solved everywhere. Regulation varies. Education lags.
Energy concerns push networks toward efficiency. User experience still matters more than protocol elegance.
None of these stop adoption. They shape where it happens first.
What the Future of Blockchain Looks Like Beyond 2026
Blockchain becomes boring. That’s success.
It fades into infrastructure alongside cloud computing and networking. The conversation moves from “what is blockchain?” to “why would we do this without it?”
Final Thoughts Before You Bet on the Blockchain Future
Blockchain in 2026 isn’t a revolution you watch. It’s one you inherit.
The industries disrupted aren’t collapsing. They’re adapting. The winners won’t talk the loudest. They’ll ship systems that work.
If you want to understand blockchain’s future, stop watching price charts. Start watching processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which industry is most likely to be disrupted by blockchain by 2026?
Finance leads the list, followed closely by supply chain, healthcare, and government services. These sectors depend on trust, verification, and multi-party coordination. Blockchain removes friction in all three. Banking uses it for settlement. Logistics uses it for traceability. Healthcare uses it for secure data access. The disruption happens because blockchain replaces slow reconciliation with shared truth.
How is blockchain revolutionizing traditional business networks?
Traditional networks rely on separate databases and constant reconciliation. Blockchain replaces that with a shared ledger everyone can verify in real time. Smart contracts automate enforcement. Disputes shrink. Costs drop. Businesses don’t need to trust each other anymore. They trust the system.
What is the future of blockchain in 2026?
By 2026, blockchain becomes infrastructure, not hype. Most users won’t see it directly. It runs behind payment systems, identity platforms, supply chains, and enterprise software. Adoption focuses on efficiency, compliance, and automation rather than speculation or buzzwords.
Will cryptocurrency and blockchain disrupt traditional financial systems?
Yes, but through modernization, not replacement. Banks adopt blockchain for faster settlement and lower costs. Cryptocurrencies influence design, while regulated systems handle scale and compliance. The disruption changes how money moves, not who controls the system overnight.
Is blockchain still considered a new technology?
No. The technology is over a decade old. What’s new is maturity. Scalability, interoperability, privacy tools, and enterprise integration reach usable levels by 2026. Blockchain stops being experimental and starts being operational.
What are the most important blockchain future trends?
Key trends include interoperability between chains, Layer-2 scaling, privacy-preserving cryptography, tokenized real-world assets, and tighter integration with AI systems. These trends matter because they solve real business constraints.
What upcoming blockchain technologies should businesses watch?
Zero-knowledge proofs, smart contract automation, tokenized assets, decentralized identity systems, and enterprise blockchain platforms stand out. These technologies move blockchain from pilots into production environments.
What are the biggest blockchain opportunities in 2026?
Opportunities exist in enterprise software, compliance automation, supply chain tracking, digital identity, and asset tokenization. The strongest opportunities focus on solving operational problems, not launching new coins.
Is blockchain mainly about cryptocurrency?
No. Cryptocurrency is one application. Blockchain itself is about shared, tamper-resistant records. Many enterprise and government systems use blockchain without any public cryptocurrency involved.
What are the main challenges slowing blockchain adoption?
Scalability limits, regulatory uncertainty, user education, and integration complexity remain challenges. However, none of these stop adoption. They simply determine where and how fast blockchain is deployed.
Will blockchain still matter after 2026?
Yes. After 2026, blockchain becomes boring in the best way. It blends into infrastructure like cloud computing. When systems depend on transparency and automation, blockchain becomes the default choice, not the exception
