6G technology is the next generation of wireless communication designed to deliver terabit-level speeds, near-zero latency, and AI-native networks. Expected in the early 2030s, 6G will enable real-time applications such as remote surgery, smart cities, digital twins, and seamless human-machine communication beyond the limits of 5G.
Quick Technology Facts
| Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Full Form of 6G | Sixth Generation wireless technology |
| Expected Launch Period | Early 2030s (research and standardization ongoing) |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps) in ideal conditions |
| Latency Target | As low as 0.1 milliseconds |
| Core Technology | AI-native networks with built-in machine learning |
| Main Advantage Over 5G | Predictive, self-optimizing networks with near-instant response |
| Key Frequency Range | Terahertz (THz) spectrum |
| Leading Countries | China, United States, South Korea, European Union |
| Leading Focus Areas | AI integration, terahertz communication, smart infrastructure |
| Example Use Case | Remote robotic surgery with real-time control |
| Current Availability | Research and testing phase only |
| 6G Mobile Phones | Not available yet |
| Major Challenges | Energy use, infrastructure cost, spectrum regulation |
| Relation to 7G | No official 7G network announced |
Why 6G matters more than you think
Every generation of wireless tech arrives quietly, then reshapes daily life. 3G put the internet in our pockets. 4G made video normal. 5G unlocked real-time apps, cloud gaming, and massive IoT. Now comes 6G, and this one is different.
Here’s what matters. The world is hitting the limits of current networks. By 2030, global data traffic is expected to be over 10× higher than today. AI systems, autonomous machines, digital twins, and immersive media all need something today’s networks struggle to deliver: instant response at massive scale.
6G is not just “faster 5G.” It’s a shift in how networks think, adapt, and interact with humans and machines. Researchers are designing 6G to work with AI, not just carry AI data. That’s the leap.
What is 6G explained in simple terms
6G stands for Sixth Generation wireless technology. It is the next evolution after 5G, expected to roll out commercially in the early 2030s.
In plain English:
6G is a network that reacts in real time, predicts demand, and connects the physical and digital worlds as one system.
Instead of just sending data from point A to point B, 6G networks will:
- Sense their environment
- Learn from traffic patterns
- Adjust automatically using AI
Think of it less like a road and more like a living traffic system that anticipates where every car will go.
The emergence of 6G: how it started early
Work on 6G began before 5G was fully deployed. That’s not unusual. Each generation starts about a decade early.
Research labs, universities, and telecom companies realized something important:
5G could not scale infinitely. Ultra-low latency, global coverage, and AI-heavy workloads demanded a new foundation.
Countries began funding early research programs around 2018–2020. Today, international standards discussions are happening through bodies like International Telecommunication Union, which will define what officially counts as 6G.
How fast will 6G internet be?
Speed headlines grab attention, so let’s ground this.
Expected 6G speeds:
- Peak data rates: up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps)
- Latency: as low as 0.1 milliseconds
That’s up to 100× faster than 5G under ideal conditions.
But raw speed is not the real story. The breakthrough is consistent performance. With 6G, applications like remote surgery or autonomous coordination don’t just work fast once. They work fast all the time.
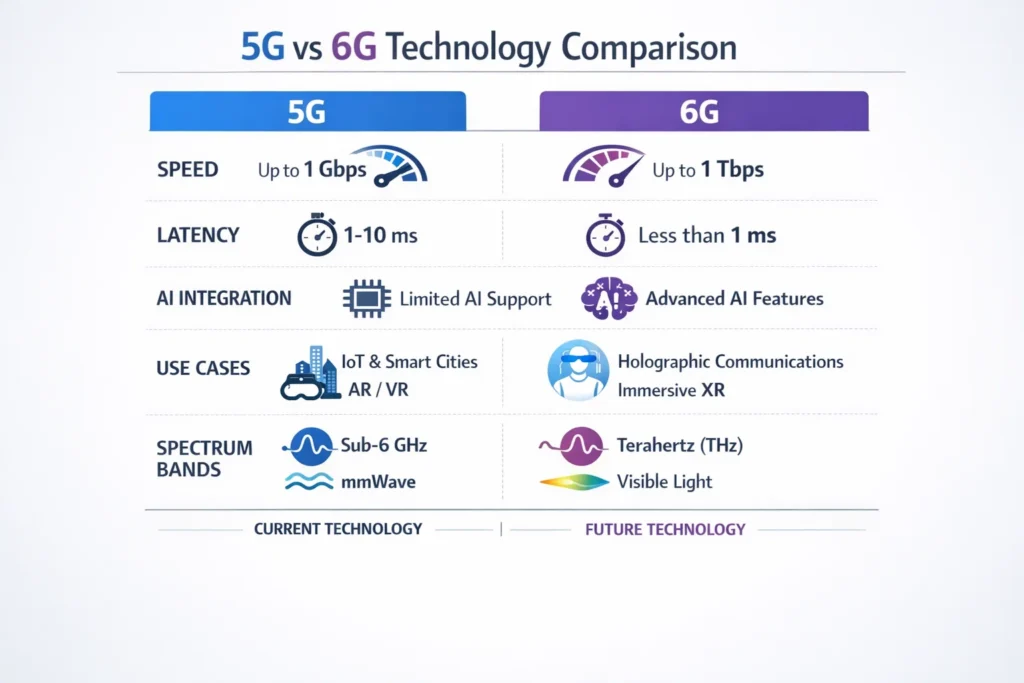
The main advantage of 6G over 5G
Here’s the bottom line: 6G is AI-native.
5G uses AI to optimize parts of the network.
6G builds AI into the network’s core decision-making.
Key advantages include:
- Self-optimizing networks
- Near-zero latency at scale
- Seamless integration of sensing, communication, and computing
In practice, this means networks that adapt instantly to demand instead of reacting after congestion happens.
Will 6G use AI? Absolutely – and deeply
AI isn’t an add-on in 6G. It’s the brain.
6G networks will use machine learning to:
- Predict traffic before it appears
- Allocate spectrum dynamically
- Detect faults and fix them automatically
- Optimize energy use in real time
This turns networks into autonomous systems rather than manually tuned infrastructure. That’s why many researchers call 6G a cognitive network.
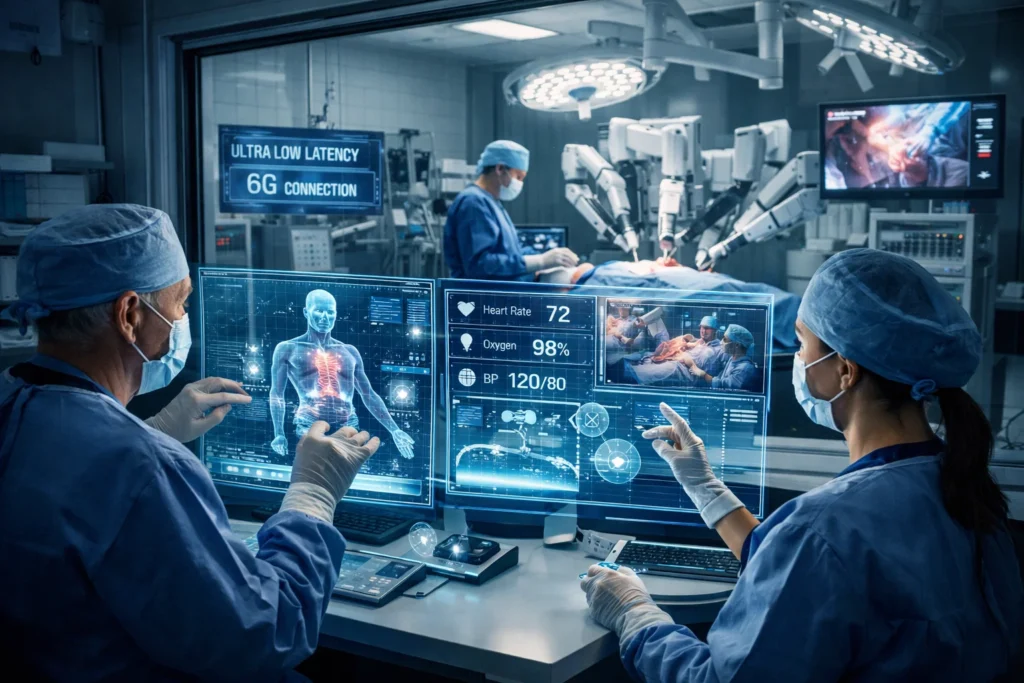

One real example of how 6G could be used
Picture a hospital where a specialist operates on a patient thousands of miles away using robotic tools.
With 5G, delays and packet loss remain risks.
With 6G, latency becomes nearly imperceptible.
The surgeon’s hand movement and the robot’s response feel simultaneous. No buffering. No hesitation. This same principle applies to coordinated drones, smart factories, and emergency response systems.
Which country is leading in 6G?
No single country “owns” 6G, but some are clearly ahead in research investment.
Key leaders include:
- China with large-scale testbeds and early terahertz trials
- The United States through university-industry partnerships
- South Korea with aggressive wireless roadmaps
- The European Union via collaborative research frameworks
Each region focuses on different strengths, from hardware to AI integration.
Which company is leading in 6G technology?
Right now, leadership is about research, not products.
Major contributors include:
- Nokia through advanced wireless labs
- Samsung with terahertz experiments
- Huawei investing heavily in core network research
No consumer company “sells” 6G yet. This phase is about patents, standards, and prototypes.
What are the disadvantages of 6G?
Every leap has trade-offs.
Challenges include:
- Energy demand: higher frequencies require smarter efficiency
- Infrastructure cost: new antennas and spectrum access
- Privacy concerns: AI-driven networks must handle data responsibly
- Regulation: terahertz spectrum needs global coordination
These aren’t deal-breakers, but they explain why deployment takes time.
Is there a 6G cell phone yet?
No. And that’s expected.
Consumer devices appear after standards stabilize and networks exist. Today’s smartphones can’t access terahertz bands or AI-native network functions.
Early 6G devices may not even look like phones. Wearables, AR glasses, and embedded sensors could lead the shift.
Is there a 7G network after 6G?
Researchers already discuss it, but cautiously.
Network generations follow real needs, not marketing numbers. 7G would only emerge when 6G reaches its limits. For now, the focus is building 6G correctly, not rushing the next label.
How 6G will change the world in practical terms
Here’s what will feel different:
- Digital and physical spaces blend seamlessly
- Machines coordinate without human oversight
- AI services respond instantly anywhere on Earth
- Connectivity reaches air, sea, space, and remote regions
This isn’t about faster downloads. It’s about systems that feel present, aware, and responsive.
Final thoughts before 6G becomes reality
6G is not arriving tomorrow, and that’s a good thing. The research phase is where the hard problems get solved.
What makes 6G exciting is not speed hype. It’s the idea of networks that understand context, anticipate needs, and quietly make complex systems feel simple.
When 6G finally reaches everyday users, most people won’t notice the technology itself. They’ll notice that things just work, instantly, everywhere. That’s how real breakthroughs usually arrive.
Frequently Asked Questions About 6G Technology
What is 6G technology explained?
6G is the sixth generation of wireless communication technology that will replace 5G. It is designed to deliver ultra-high speeds, near-zero latency, and AI-driven network intelligence, enabling advanced applications like holographic communication, digital twins, and autonomous systems.
What is the full form of 6G?
The full form of 6G is Sixth Generation wireless technology. It represents the next stage in the evolution of mobile and wireless networks after 5G.
How fast will 6G internet be?
6G internet is expected to reach peak speeds of up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps) under ideal conditions. Latency could drop to as low as 0.1 milliseconds, making communication feel almost instantaneous.
What is the main advantage of 6G over 5G?
The main advantage of 6G over 5G is that it is AI-native. Artificial intelligence will be built directly into the network core, allowing self-optimization, predictive traffic control, and real-time decision-making without human intervention.
Will 6G use AI?
Yes, 6G will heavily rely on artificial intelligence. AI will manage network traffic, predict demand, optimize spectrum usage, detect faults, and improve energy efficiency automatically.
How will 6G change the world?
6G will enable real-time digital interaction at a global scale. It will support smart cities, remote surgery, autonomous transportation, immersive virtual environments, and seamless communication between humans, machines, and digital systems.
What is one example of how 6G is used?
One example of 6G use is remote robotic surgery, where doctors can operate from thousands of miles away with no noticeable delay, thanks to ultra-low latency and AI-managed network reliability.
Which country is leading in 6G technology?
No single country fully leads 6G, but China, the United States, South Korea, and European Union nations are currently at the forefront of research, testing, and early development.
Which company is leading in 6G technology?
Several companies are leading 6G research, including major telecom and technology firms. Leadership is currently focused on research labs, patents, and standards rather than commercial products.
What are the disadvantages of 6G?
The main disadvantages of 6G include high infrastructure costs, increased energy demands, complex spectrum regulation, and potential privacy concerns due to AI-driven data processing.
Is there a 6G cell phone?
No, there is currently no 6G cell phone available. 6G networks are still in the research phase, and consumer devices will only appear after standards and infrastructure are finalized, likely in the early 2030s.
What is the future scope of 6G technology?
The future scope of 6G includes smart cities, space-air-ground connectivity, advanced healthcare, industrial automation, immersive virtual environments, and global AI-powered communication systems.
Is there a 7G network after 6G?
There is no official 7G network yet. Researchers may explore future generations, but 7G will only emerge when 6G reaches its technological limits, which is expected many years after 6G deployment.
