Emerging tech in space exploration refers to advanced tools like AI, autonomous systems, new propulsion, and smart sensors that enable deeper, longer, and safer missions. It matters today because space missions now rely on machines to think and act independently. These technologies will shape long-term lunar bases, Mars missions, and deep-space discovery.
Facts on Emerging Tech in Space Exploration
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Advanced technologies enabling modern and future space missions |
| Core Technologies | AI systems, robotics, propulsion, satellites, deep-space communication |
| Main Use Cases | Planetary exploration, space telescopes, asteroid missions |
| Key Advantage | Autonomy, efficiency, and longer mission lifespan |
| Leading Players | NASA, ISRO, ESA, China CNSA |
| Current Status | Actively used in ongoing missions |
| Future Direction | Human–robot collaboration and deep-space exploration |
Emerging Tech in Space Exploration: Innovations & Beyond:
Here’s what matters. Space exploration is no longer just about rockets and brave astronauts. It’s about intelligence, autonomy, data, and endurance. The real breakthroughs today happen quietly inside software, sensors, and materials that allow machines to go farther, think faster, and survive longer than humans ever could.
According to international space agencies, more than 90 countries now operate satellites. Private launch activity has multiplied in a decade. At the same time, missions are shifting from short-term exploration to long-duration science. That shift only works because emerging technology fills the gap between ambition and physics.
Let me explain how this new space era actually works.
Why space exploration technology matters right now
Space has become crowded, competitive, and expensive. Every mission must deliver results with fewer failures and tighter budgets. That pressure forces innovation.
Modern probes operate millions or even billions of kilometers away. Human control is slow at that distance. Signals can take minutes or hours. So spacecraft must make decisions on their own. That single fact explains why AI, autonomy, and smart systems now sit at the center of space exploration.
There’s another driver too. We’re no longer asking simple questions like “Is there water?” We’re asking harder ones. How do planets form? Can life exist beyond Earth? What is dark matter made of? Those questions demand better instruments, cleaner data, and longer missions.
Technology is the only way forward.
What are emerging technologies in space exploration?
Emerging technologies in space exploration are tools and systems that did not exist, or were not reliable, a decade ago. They allow spacecraft to operate independently, travel farther, and study space with precision humans cannot match.
These technologies share three traits. They reduce risk. They extend mission life. They multiply scientific output.
Here’s a clear way to see the shift.
| Problem | Traditional Limitation | Emerging Tech Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Signal delay | Human control too slow | AI-based autonomy |
| High launch cost | Single-use rockets | Reusable launch systems |
| Fragile instruments | Short mission lifespan | Advanced materials |
| Limited data | Narrow sensors | AI-enhanced analysis |
This is not incremental change. It’s a redesign of how exploration works.
The five core technologies powering modern space missions
Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems
AI allows spacecraft to navigate, diagnose faults, and prioritize data without waiting for Earth. Mars rovers already choose which rocks to study. Future probes will decide entire mission paths on their own.
Advanced propulsion
Ion drives, solar sails, and nuclear thermal concepts offer slow but efficient thrust. These systems trade speed for endurance, which matters for deep-space missions.
Space robotics
Robotic arms, autonomous landers, and swarm robots handle tasks too dangerous or distant for humans. Precision robotics also reduce mission mass and cost.
Next-generation satellites
Smaller, smarter satellites work in constellations. They share data, reroute signals, and recover from failures automatically.
Deep-space communication
Laser-based communication promises faster, cleaner data transfer across extreme distances, replacing traditional radio-only systems.
Together, these five technologies form the backbone of modern exploration. 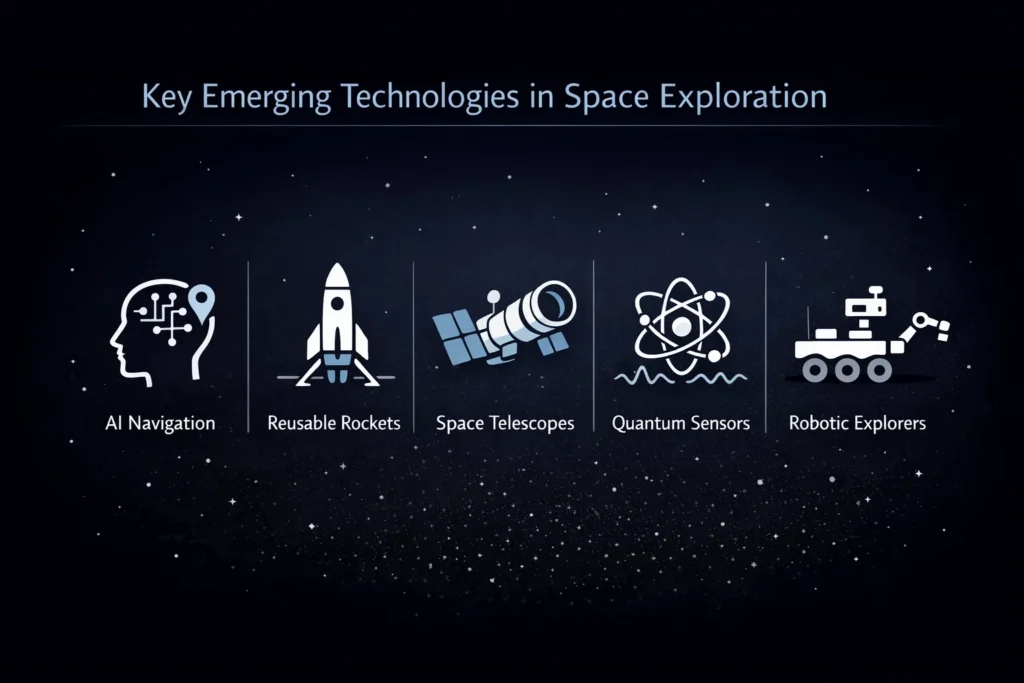
Latest developments in space exploration
The past few years delivered major milestones. The James Webb Space Telescope opened a new window into the early universe, detecting galaxies formed shortly after the Big Bang and analyzing exoplanet atmospheres in detail never seen before.
Mars exploration moved from surface imaging to sample return planning. Asteroid missions brought physical material back to Earth for laboratory study. Lunar missions shifted from flags and footprints to long-term presence and resource testing.
What ties all of this together is automation. These missions succeed because machines now handle complexity that once required constant human input.
Which technology is used to explore space beyond our solar system?
Beyond our solar system, speed matters less than intelligence. Probes traveling that far must survive decades with no repair and limited communication.
Key technologies include:
- Autonomous navigation systems that adjust course using onboard sensors
- Radiation-hardened electronics that withstand deep-space exposure
- AI-driven data filtering that sends only the most valuable findings back to Earth
Interstellar exploration is slow by necessity. Emerging technology ensures it is not blind or wasteful.
Who leads the world in space technology?
Leadership depends on what you measure.
The United States, driven by NASA and private industry, leads in deep-space science, reusable launch systems, and planetary exploration.
China excels in rapid mission execution and lunar infrastructure planning.
Europe dominates precision science instruments and cooperative missions.
India, through ISRO, stands out for cost efficiency and engineering discipline, delivering reliable missions on limited budgets.
No single country owns the future of space. The edge comes from combining public science with private innovation.

NASA, ISRO, and the next wave of space projects
NASA’s newest projects focus on sustained exploration. Lunar gateway stations, Mars sample return missions, and advanced space telescopes aim to support long-term research rather than one-time achievements.
ISRO is advancing small satellite launch systems, interplanetary probes, and Earth-observation technology that feeds climate and disaster data back home. Its success shows that emerging tech is not only about scale. It’s about smart design.
Both agencies rely heavily on automation, AI-driven diagnostics, and modular spacecraft architecture. That trend will only accelerate.
Big questions people ask about space
Is Planet 9 confirmed?
No. Planet 9 remains a hypothesis based on gravitational effects observed in distant objects. No direct observation exists yet.
Why is 95% of the universe invisible?
Most of the universe consists of dark matter and dark energy. They do not emit light, so scientists infer their presence through gravitational effects rather than direct observation.
What is the newest thing discovered in space?
Recent discoveries include complex organic molecules in distant star-forming regions and detailed atmospheric signatures on exoplanets, hinting at chemical processes once thought rare.
These answers exist because instruments now see what older technology could not.
Emerging trends in the aerospace sector
Three trends dominate aerospace innovation.
First, autonomy replaces manual control. Systems that learn and adapt outperform scripted commands.
Second, sustainability matters. Reusable rockets, debris tracking, and longer-lasting satellites reduce orbital clutter and cost.
Third, data beats hardware. Smarter analysis often delivers more value than bigger machines.
Aerospace is becoming a software-driven field with hardware as the platform, not the focus.
What space exploration looks like in the next 20 years
Human presence will expand slowly. Robotic presence will explode.
Expect permanent lunar infrastructure supported by autonomous systems. Mars missions will rely heavily on robotic preparation before humans arrive. Deep-space probes will operate as independent scientists, not remote tools.
Risk remains. Space is hostile, and technology fails. But emerging tech shifts the odds. It turns exploration from a gamble into a calculated experiment.
Practical checklist: key space technologies to watch
- AI-based spacecraft autonomy
- Laser communication systems
- Reusable and modular launch vehicles
- Radiation-resistant materials
- Robotic surface exploration systems
If a mission uses most of these, it’s built for the future.
Final thoughts before looking to the stars
Space exploration is no longer limited by curiosity. It’s limited by capability. Emerging technology expands that capability quietly, relentlessly, and intelligently.
The next great discoveries will not come from bigger rockets alone. They will come from smarter machines, better data, and systems designed to think when humans cannot be there.
That’s the real innovation beyond the stars.
FAQs: Emerging Tech in Space Exploration
What are the emerging technologies in space exploration?
Emerging technologies include artificial intelligence, autonomous navigation, advanced propulsion systems, space robotics, next-generation satellites, and laser-based deep-space communication. These tools allow spacecraft to operate independently, travel farther, and collect higher-quality data with less human intervention.
Which technology is used to explore space beyond our solar system?
Deep-space exploration relies on autonomous probes, radiation-hardened electronics, AI-driven navigation, and long-duration propulsion systems like ion drives. These technologies help spacecraft survive extreme distances where real-time human control is impossible.
What are the latest developments in space exploration?
Recent developments include advanced space telescopes studying early galaxies, asteroid sample return missions, reusable launch vehicles, and AI-assisted planetary rovers. These advances focus on long-term science rather than short, one-off missions.
What are the five technologies needed for space exploration?
The five core technologies are artificial intelligence, advanced propulsion, space robotics, smart satellites, and deep-space communication systems. Together, they support navigation, data collection, mission safety, and long-term exploration.
Which country is number one in space technology?
There is no single number one country. The United States leads in deep-space science and private innovation, China excels in rapid mission execution, Europe dominates scientific instruments, and India is known for cost-efficient and reliable missions.
What are the future projects in space exploration?
Future projects include sustained lunar bases, Mars sample return missions, space-based observatories, asteroid mining research, and robotic preparation for human missions to Mars and beyond.
What is the newest thing discovered in space?
Recent discoveries include detailed chemical signatures in exoplanet atmospheres and complex organic molecules in distant star-forming regions, suggesting that the building blocks of life may be more common than once thought.
Is Planet 9 confirmed?
No. Planet 9 remains a hypothesis based on unusual orbital patterns of distant objects. Astronomers have not directly observed the planet yet.
Why is 95% of the universe invisible?
Most of the universe consists of dark matter and dark energy, which do not emit light. Scientists detect them indirectly through their gravitational effects on visible matter.
What are the four main space technologies?
The four commonly cited space technologies are launch systems, spacecraft and satellites, communication systems, and navigation and control technologies. Emerging tech improves each of these areas.
Who has the most advanced space technology?
Agencies like NASA and ISRO, along with European and Chinese space programs, are among the most advanced. Private companies also play a major role, especially in launch systems and satellite technology.
What is NASA’s newest focus?
NASA’s recent focus includes long-term lunar exploration, Mars sample return planning, advanced space telescopes, and greater use of AI and autonomous systems in missions.
What are the emerging trends in the aerospace sector?
Key trends include automation, AI-driven mission control, reusable launch vehicles, sustainable space operations, and increased collaboration between public agencies and private companies.
What is the new technology in ISRO?
ISRO is advancing small satellite launch systems, autonomous navigation, interplanetary mission design, and cost-efficient spacecraft engineering, making complex missions achievable on limited budgets.
